Rune Command Line Reference
The rune CLI tool is the primary way most people will develop Runes.
Model Info (rune model-info)
The first step when integrating a TensorFlow Lite model into a Rune is to figure out what data it receives as input and what it generates as output.
Often this information will already be known (e.g. because the model was
developed in-house or well documented), but it is also possible to use the
rune model-info sub-command to inspect a TensorFlow Lite model.
$ rune model-info --help
Load a TensorFlow Lite model and print information about it
USAGE:
rune model-info [OPTIONS] <file>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-f, --format <format> The format to print output in (supported: json, text) [default: text]
ARGS:
<file> The TensorFlow Lite model to inspect
The Model (<file>)
The mode file is a required positional argument pointing to a valid TensorFlow Lite file.
Output Format (--format)
By default, the model's inputs and outputs will be presented in a human-readable
format. This is the equivalent of using the --format text option.
$ rune model-info ./yamnet.tflite
Ops: 114
Inputs:
waveform: Float32[1]
Outputs:
Identity: Float32[1, 521]
Identity_1: Float32[1, 1024]
Identity_2: Float32[1, 64]
The --format json flag can be provided to get a more machine-friendly version.
$ rune model-info microspeech.tflite --format json
{
"inputs": [
{
"name": "Reshape",
"element_kind": "Int8",
"dims": [
1,
1960
]
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "labels_softmax",
"element_kind": "Int8",
"dims": [
1,
6
]
}
],
"ops": 4
}
In either case, the inputs and outputs properties specify the tensor
dimensions and element types used as input/output. The possible values for
element_kind correspond to the TfLiteType enum variants in tensorflow/tensorflow/lite/c/c_api_types.h header file, and are
named similarly to that used in the outputs
section of a Runefile.
Build (rune build)
The rune build sub-command will parse a Runefile and generate an equivalent
project in Rust so it can be compiled to WebAssembly.
$ rune build --help
Compile a Runefile into a Rune
USAGE:
rune build [FLAGS] [OPTIONS] [runefile]
FLAGS:
--debug Compile the Rune without optimisations
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
--cache-dir <cache-dir> The directory to use when caching builds [env: CACHE_DIR=]
-c, --current-dir <current-dir> The directory that all paths are resolved relative to (Defaults to the Runefile's
directory) [env: CURRENT_DIR=]
-n, --name <name> The name of the Rune (defaults to the Runefile directory's name)
-o, --output <output> Where to write the generated Rune
ARGS:
<runefile> The Runefile to compile [default: Runefile.yml]
The Runefile (<runefile>)
The name of the runefile being compiled. This is the only positional argument
and will default to Runefile.yml in the current directory.
The Cache Directory (--cache-dir)
The --cache-dir argument is used to specify a temporary directory that the
Rune project will be written to and compiled in. If not specified then
a rune named sine would use the runes/sine/ directory inside
the operating system's native cache directory.
| Platform | OS Cache Directory | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Linux | $XDG_CACHE_HOME or $HOME/.cache | /home/alice/.cache/runes/sine |
| macOS | $HOME/Library/Caches | /Users/Alice/Library/Caches/runes/sine |
| Windows | {FOLDERID_LocalAppData} | C:\Users\Alice\AppData\Local\runes\sine |
The Current Directory (--current-directory)
The --current-directory argument specifies which directory to use when
resolving relative paths in a Runefile. By default it will be the directory the
Runefile is located in.
Name (--name)
Each Rune can be given a name which alters things like the name of the generated Rust project and the label attached to any log messages emitted by the Rune. By default, the name of the Runefile's directory will be used.
Output File (--output)
The --output argument specifies where the generated Rune will be saved to. By
default it will be the name with the .rune extension (e.g.
microspeech.rune).
Debug Mode (--debug)
A Rune can be compiled with debug assertions enabled and without optimisations
using the --debug flag.
This is typically used when working on a new proc block because it enables more useful stacktraces (stack frames won't be inlined away) and lets the author perform more assertions that are too expensive to be present in a release build but may be helpful during development.
Compiling a Rune in debug mode will often be faster than release mode (the default), however Runes dealing with larger amounts of data may become unacceptably slow to execute.
Run (rune run)
The rune run sub-command takes a compiled Rune and runs it. This
specified capabilities as inputs.
This is typically done when an engineer is prototyping locally or wanting an easy way to run Runes on a server. For most other use cases, application engineers will gain more fine-grained control by embedding a Rune Virtual Machine directly into their applications.
$ rune run -h
Run a rune
USAGE:
rune run [OPTIONS] <rune>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-c, --capability <capabilities>... Pass information to a capability as `key:value` pairs
-r, --repeats <repeats> The number of times to execute this rune [default: 1]
ARGS:
<rune> The Rune to run
The Rune (<rune>)
The Rune file is a required argument pointing to a valid Rune on disk.
Capabilities (--capability)
By design, the only way to pass information into a Rune is via a
Capability. The syntax for specifying a capability is --capability
image:person.png, where the --capability parameter can be passed multiple
times and its value is in the form, key:value.
$ run gesture.rune --capability accel:example_ring.csv
The capabilities supported by the rune CLI are:
| Key | Input/Extension |
|---|---|
accelerometer |
|
image |
|
random |
|
raw |
|
sound |
|
Inspect (rune inspect)
Each Rune will be embedded a serialised version of the original Runefile and
version of the rune CLI it was compiled from.
This metadata can be retrieved later on using the rune inspect subcommand
although tools like wasm-strip may remove it to reduce the Rune's size.
$ rune inspect -h
Inspect a Rune
USAGE:
rune inspect [OPTIONS] <rune>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-f, --format <format> The format to use when printing output [default: text] [possible values: json, text]
ARGS:
<rune> The Rune to inspect
Rune (<rune>)
The compiled Rune to inspect.
Format (--format)
By default, the model's inputs and outputs will be presented in a human-readable
format. This is the equivalent of using the --format text option.
$ rune inspect examples/debugging/debugging.rune
Compiled by: rune v0.2.1 (ebb8057 2021-05-29)
Capabilities:
rand (Random)
Outputs:
- f32[1]
The --format json flag can be provided to get a more machine-friendly version.
$ rune inspect examples/debugging/debugging.rune --format json
{
"rune_cli_build_info": {
"timestamp": "2021-05-29T08:16:05.317354345Z",
"profile": "debug",
"optimization_level": 0,
"crate_info": {
"name": "rune",
"version": "0.2.1",
"authors": [
"Kartik Thakore <kartik@thakore.ai>",
"Akshay Sharma <akshay@sharma.ai>",
"Michael-F-Bryan <michael@hotg.ai>"
],
"license": "Apache 2.0",
"enabled_features": [],
"available_features": [],
"dependencies": []
},
"compiler": {
"version": "1.54.0-nightly",
"commit_id": "881c1ac408d93bb7adaa3a51dabab9266e82eee8",
"commit_date": "2021-05-08",
"channel": "Nightly",
"host_triple": "x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu",
"target_triple": "x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu"
},
"version_control": {
"Git": {
"commit_id": "0e5c7076baa5c4075db94a778020ad47bbbe8672",
"commit_short_id": "0e5c7076ba",
"commit_timestamp": "2021-05-29T08:13:36Z",
"dirty": false,
"branch": "master",
"tags": []
}
}
},
"simplified_rune": {
"capabilities": {
"rand": {
"capability_type": "Random",
"outputs": [
{
"type": "f32",
"dimensions": [
1
]
}
],
"parameters": {}
}
}
}
}
Graph (rune graph)
The rune graph subcommand can be used to visually explore a Rune pipeline.
When directed at a Runefile or compiled Rune, this will generate a file that
graphviz can turn into a flow chart.
$ rune graph -h
Visualise a Rune's pipeline graph
USAGE:
rune graph [OPTIONS] <input>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-o, --output <output> Where to write the generated file (stdout by default)
ARGS:
<input> The Rune or Runefile to graph
The output from running rune graph on a Runefile
will typically be passed directly to the dot command.
$ rune graph examples/debugging/Runefile.yml | dot -Tpng > debugging.png
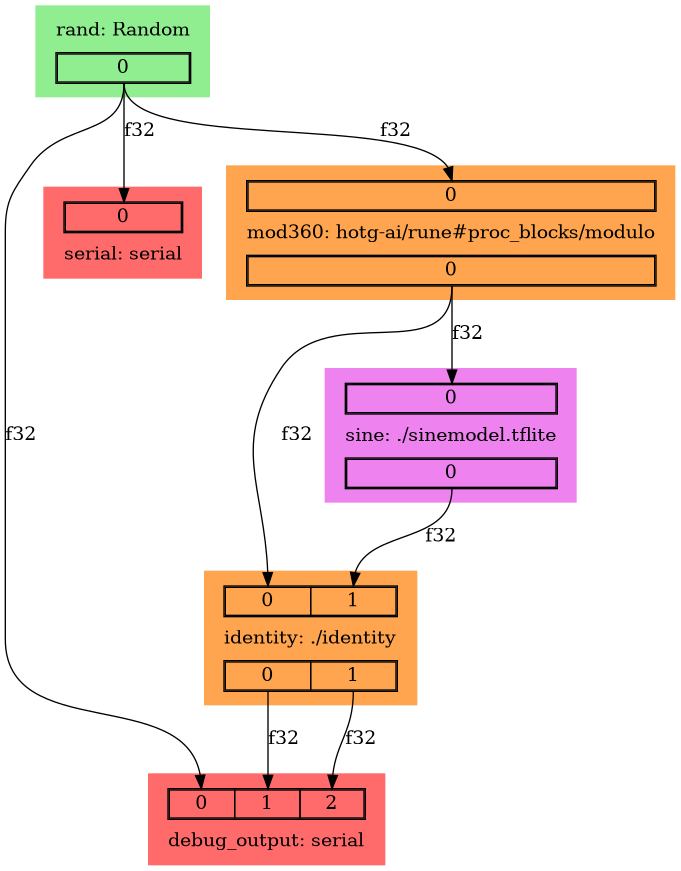
Input (<input>)
The Rune or Runefile to analyse and graph.
Output File (--output)
The --output argument specifies where the generated DOT file will be written
to. If this argument isn't provided it will be printed to STDOUT.
Version (rune version)
The rune version sub-command prints out the rune binary's version number.
$ rune version --help
Print detailed version information
USAGE:
rune version [FLAGS] [OPTIONS]
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
-v, --verbose
OPTIONS:
-f, --format <format> [default: text]
By default, it will just print the version number, build date, and the git commit it was compiled from.
$ rune version
rune 0.2.1 (8fbe8a5 2021-05-21)
For more detailed information including when the rune binary was compiled and
which version of the Rust compiler it was compiled with, use the --verbose
flag. By default, this information will be printed in a human-readable form
(i.e. equivalent to --format text).
$ rune version --verbose
rune 0.2.1 (8fbe8a5 2021-05-21)
binary: rune
rune-version: 0.2.1
commit-hash: 8fbe8a518875312dd7e39a092d0b4d7482fbaee8
commit-date: 2021-05-21T18:32:12+00:00
host: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
rustc-version: 1.54.0-nightly
rustc-commit-hash: 881c1ac408d93bb7adaa3a51dabab9266e82eee8
rustc-commit-date: 2021-05-08
The --format json argument can be used to ask for output in a machine-readable
form.
$ rune version --verbose --format json
{
"executable": "rune",
"rune-version": "0.2.1",
"commit-short-hash": "8fbe8a5",
"commit-hash": "8fbe8a518875312dd7e39a092d0b4d7482fbaee8",
"commit-timestamp": "2021-05-21T18:32:12Z",
"host": "x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu",
"rustc-version": "1.54.0-nightly",
"rustc-commit-hash": "881c1ac408d93bb7adaa3a51dabab9266e82eee8",
"rustc-commit-date": "2021-05-08"
}