Yolo
An object detection model that localizes objects in an image on the edge.
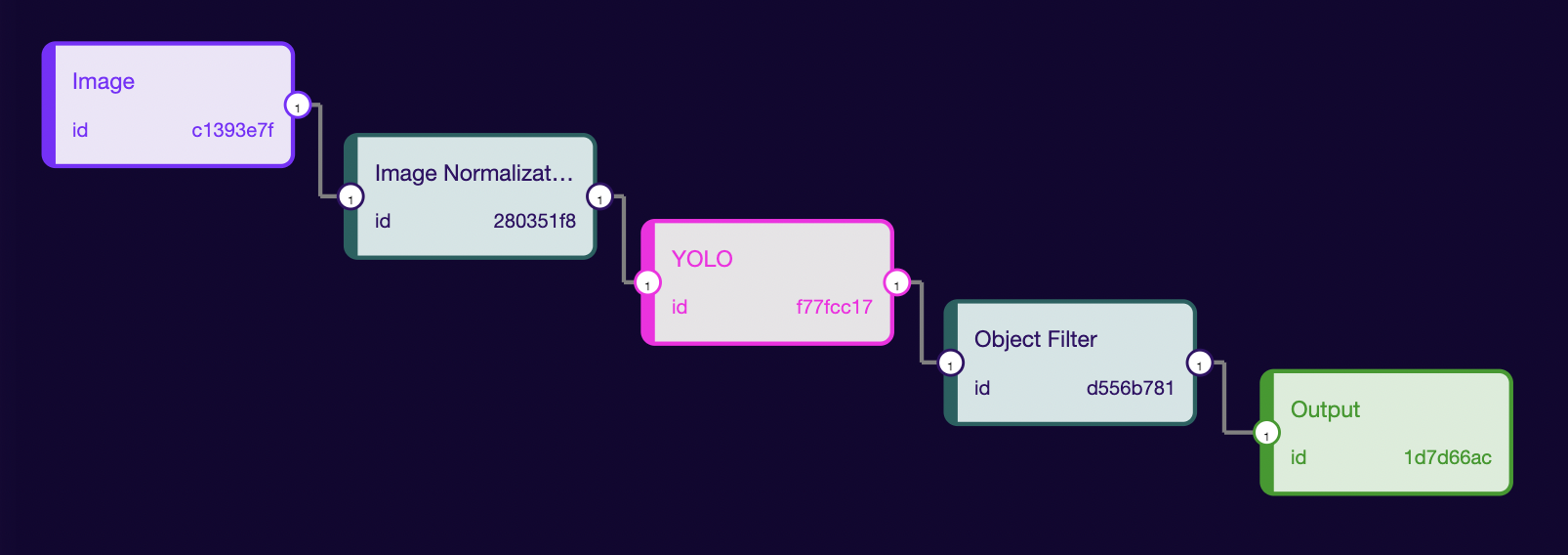
The first step of creating an ML pipeline is finding (or training) a Machine Learning Model that matches your application. Here, we have decided to choose the YOLO model. We will start by knowing the model input/output information. So, click on the model node present inside the studio with the name of the YOLO. It will show the Input/Output information. This information will be used to build the ML Pipeline.
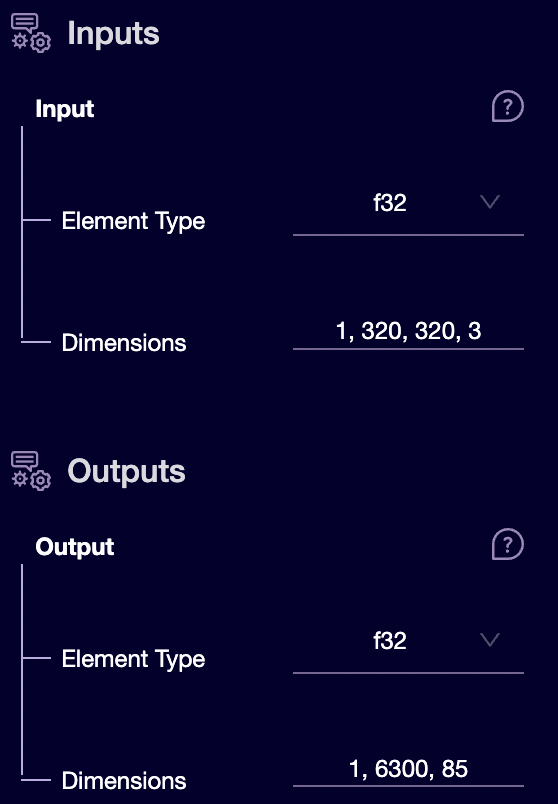
Looking at the input, we can say the model will take a 320 x 320 RGB (because the channel is 3) image as input. The input type is f32, but last time we saw that we could take u8 image as input. So, we will need a proc-bock that will convert u8 to f32 type. For this, we have image_normalization proc-block. It will take the u8 image matrix and normalize their values to the range [0, 1] as f32. We have got all our nodes sorted out for the YOLO model. The output is a 3-d tensor with format [1, num_detection, detection_box(x, y, w, h) + confidence_scores + total_detection_classes]. We can see the number of detections is 6500. It means there will be multiple bounding boxes for every single object. We will have to filter the
detected objects to:
- remove duplicate detection for a single object
- remove the objects with low confidence based on a threshold
giving a
2-dtensor with dimension[*, 6](where * is the total number of detected objects, and 6 ->[ x-coordinate, y-coordinate, h, w, confidence_value, label_index]) as output. To perform this we will use an object_filter proc-block. Perfect, now we have all our pieces in place. Let's start writing our ML Pipeline.
- Drag an image from the Input:
We will set the output type to u8 and dimensions to [1, 320, 320, 3] because, as we saw above, this is the format needed by our model.
The IMAGE takes the following arguments:
- width - the image's width in pixels
- height - the image's height in pixels
- pixel-format - the format used by the pixels. Possible values are:
- @PixelFormat::Grayscale
- @PixelFormat::RGB
- As discussed earlier, we will need a proc-block that could transform our
u8type tof32and normalize the image matrix in the range[0, 1]. Next, we will connect the Image node output to the input of this node and will define the output dimension. - Drag the YOLO model from the left side panel.
- Next, let’s drag the object_filter proc-block to filter the duplicate prediction
made by our model for an object. Set the dimensions to
[6500,6]because6500is the maximum number of objects that this model could detect. - Finally, connect the output of the label proc-block node to the input of the
Outputnode.